Sexually transmitted diseases, known as STDs, may occur before or during pregnancy and may harm the health of the mother and baby, leading to complications such as preterm labor, miscarriage, low birth weight, and delayed development.
Symptoms vary depending on the type of infection presented, but usually genital and itchy wounds. Treatment should be made according to the cause of the disease, but antibiotic and antiviral medications are usually used, under the indication of the obstetrician.
7 Major STIs in Pregnancy
The 7 major STDs that may interfere with pregnancy are:
1. Syphilis
Syphilis present during pregnancy should be treated as soon as it is identified, as there is a risk that the disease may cross the placenta and pass into the baby or cause complications such as miscarriage, low birth weight, deafness and blindness.
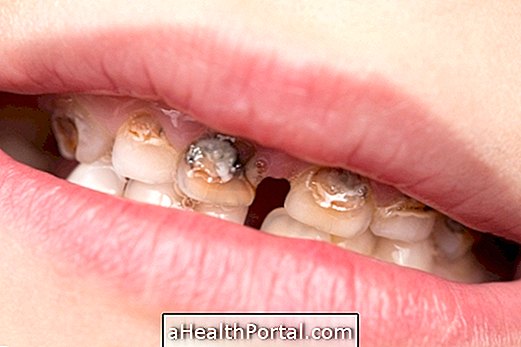
Its symptoms are the appearance of reddened wounds on the genitals, which disappear after a few weeks and reappear on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The diagnosis of the disease is made through a blood test, and its treatment is done with the use of antibiotics. Understand how the treatment and complications of syphilis are done.
2. AIDS
AIDS is a sexually transmitted disease that can be passed on to the baby during gestation, at the time of childbirth or during breastfeeding, especially if the mother does not receive adequate treatment during pregnancy.
Their diagnosis is made during the first prenatal examinations and, in positive cases, the treatment is done with drugs that decrease the reproduction of the virus in the body, such as AZT. See how the delivery should be and how to know if the baby has been infected.

3. Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea can cause complications in pregnancy such as preterm delivery, delayed fetal development, inflammation in the lungs, bronchi, or the baby's ear after delivery.
In most cases, this disease does not cause symptoms and therefore is often discovered only during prenatal care. However, some women may experience symptoms such as pain in the urine or in the lower abdomen and increase of the vaginal discharge, and their treatment is made with antibiotics. See more details of treatment here.
4. Chlamydia
Chlamydia infection is also related to complications such as premature labor, conjunctivitis and pneumonia of the newborn, causing pain when urinating, vaginal discharge with pus and pain in the lower abdomen.
She should be investigated during the prenatal exams and her treatment is also done with the use of antibiotics. Look at the possible complications of this disease here.
5. Herpes
During pregnancy, herpes increases the risk of miscarriage, microcephaly, delayed fetal growth, and contamination of the baby by congenital herpes, especially during delivery.
In this disease wounds appear in the genital region that are accompanied by burning, tingling, itching and pain, and can progress to small ulcers. The treatment is done with medicines that fight the virus, but the herpes has no definitive cure. See more about treatment here.
6. Soft cancer
The soft cancer is characterized by the appearance of several painful wounds in the genital region and the anus, and the appearance of only a deeper ulcer, sensitive and with bad smell can occur.
The diagnosis is made by scraping the wound, and the treatment uses injections or tablets of antibiotics. See the difference between soft canker and syphilis here.
7. Donovanose
Donovanose is also known as venereal granuloma or inguinal granuloma, and causes the appearance of ulcers or nodules in the genital and anal region that normally do not cause pain but worsen during pregnancy.
In most cases, it does not harm the fetus but must be treated with antibiotics so as not to spread to other parts of the body. See the remedies used here.
Prevention of the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases to the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth depends primarily on prenatal care and follow-up visits.
In addition, it is important to be aware of any changes in the genital area, and seek medical help as soon as you identify wounds, excessive vaginal discharge or itching in the genital area.