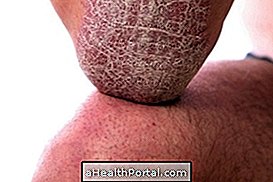
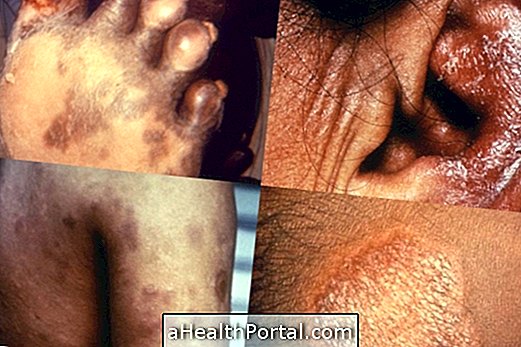
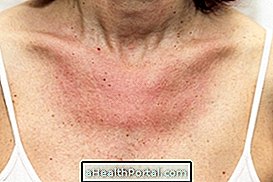
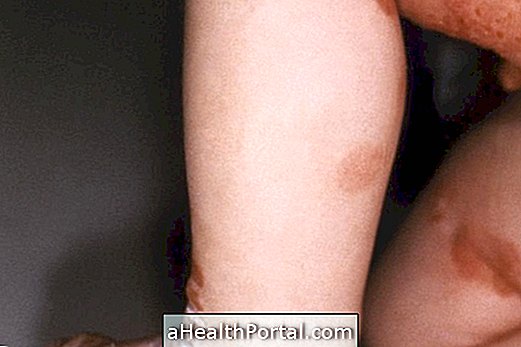
Epidermolysis bullosa is a genetic skin disease that causes the formation of blisters on the skin and mucous membranes, after any friction or minimal trauma, such as brushing skin tags or removing band-aid, for example. This is because, in people with this disease, the skin is extremely sensitive and gets injured very easily, forming painful blisters.
Depending on the layer of skin that leads to the formation of blisters, epidermolysis bullosa can be divided into 3 types:
- Epidermolysis bullosa simple : formation of bubbles due to detachment of intraepidermal region, which lies below the middle layer of the skin;
- Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophic : the bubbles arise due to the detachment of the intraderme region, which in the most superficial layer;
- Epidermolysis bullosa junctional : characterized by the formation of bubbles due to the detachment of the region between the most superficial and intermediate layer.
This type of dermatitis is not contagious and also has no cure, and its treatment must be maintained constantly, as it is the only way to relieve discomfort and prevent the appearance of new blisters.
How is the treatment done?
There is no specific treatment for epidermolysis bullosa, and it is very important to make regular consultations with the dermatologist to assess the condition of the skin and to adjust the treatment in each case.
To prevent bubbles from appearing
Since there is no cure, treatment is only done to relieve the symptoms and reduce the chances of new blisters emerging. The first step is to take some care at home, such as:
- Wear cotton clothing, avoiding synthetic fabrics;
- Remove labels from all clothing;
- Wear underwear that is reversed to prevent contact of the elastic with the skin;
- Wear shoes light and wide enough to comfortably wear socks;
- Be very careful when using towels after bathing by gently pressing the skin with a soft towel;
- Apply vaseline in abundance before removing dressings and not forcing them to withdraw;
- If clothing eventually sticks to the skin, leave the area soaked in water until the clothing releases itself from the skin;
- Sleep with socks and gloves to prevent injuries that may occur during sleep.
In addition, if skin itching occurs, your doctor may prescribe the use of corticosteroids, such as Prednisone or Hydrocortisone, to relieve inflammation of the skin and reduce symptoms, preventing it from scratching the skin, producing new lesions.
The application of botox to the feet seems to be effective in preventing blisters in this region, and gastrostomy is indicated when it is not possible to feed properly without the appearance of blisters in the mouth or esophagus.
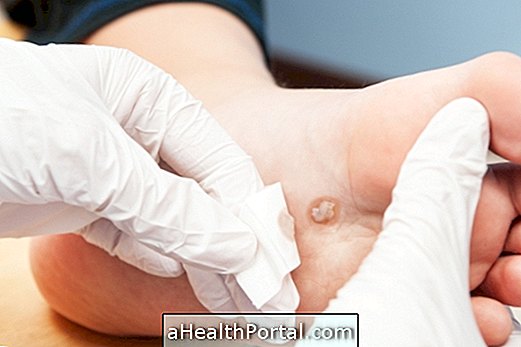
To treat existing bubbles
Existing blisters should ideally be treated at the hospital or at the health clinic by a physician or nurse in order to keep the dressing sterile and prevent the onset of infections.
However, if infections develop, the dermatologist may prescribe antibiotics to combat excess bacteria and facilitate skin healing.
When surgery is needed
Surgery for bullous dermatitis is usually indicated in case the scars left by the blisters make it difficult for the body to move or cause deformities that decrease the quality of life.
In some cases, surgery may still be used to make skin excerpts, especially on wounds that are taking a long time to heal.
Main symptoms of epidermolysis bullosa
The symptoms of epidermolysis bullosa are:
- Emergence of blisters on the skin or mucous membranes at minimal trauma;
- There may be impairment or absence of nails, decrease or absence of hair and decrease sweating or exaggerated sweating.
The eyes can also be affected by the formation of blisters, which, when it becomes frequent, can affect vision.
The diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa can be made through examinations such as skin biopsy and immunofluorescence examination or electron microscopy, which must be requested by the dermatologist.