The ASLO test, also called ASO, AEO or antistreptolysin O, aims to identify the presence of a toxin released by the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes, streptolysin O. If infection with this bacteria is not identified and treated with antibiotics, the person may develop some complications, such as glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever, for example.
The main sign of infection by this bacterium is the sore throat that happens more than 3 times a year and it takes time to be solved. In addition, if there are other symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain or pain and swelling in the joints, it is important to seek medical attention, as it may be rheumatic fever. Know what is rheumatism in the blood.
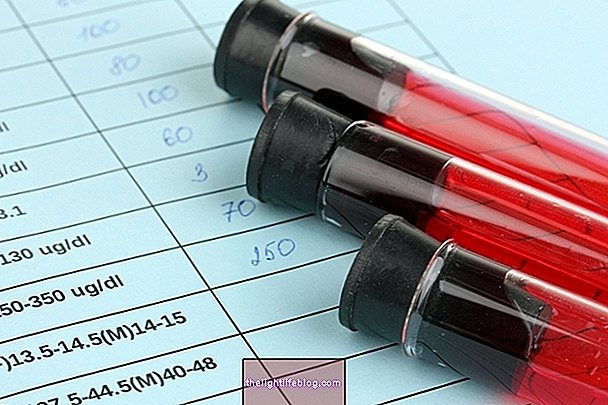
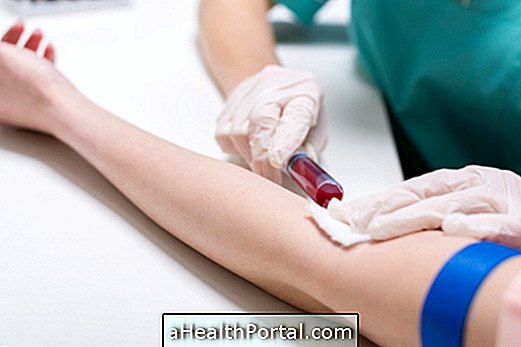
The test should be fasted for 4 to 8 hours, depending on the recommendation of the doctor or laboratory, and the result is usually released after 24 hours.
What is it for
The doctor usually asks for the ASLO exam when the person has frequent episodes of sore throat in addition to symptoms that may indicate rheumatic fever, such as:
- Fever;
- Cough;
- Shortness of breath;
- Pain and swelling of joints;
- Presence of lumps under the skin;
- Presence of red spots on the skin;
- Chest pain.
Thus, from the analysis of the symptoms and the result of the examination, the doctor can confirm the diagnosis of rheumatic fever, for example, which is characterized by the high concentration of antistreptolysin O in the blood. Understand how to identify and treat rheumatic fever.
Streptolysin O is a toxin produced by Streptococcus pyogenes, which can cause rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, scarlet fever and tonsillitis, if it is not identified or treated with antibiotics. Thus, the main means of diagnosis of infection by this bacterium is from the identification of this toxin through the detection of antibodies produced by the body against the bacterium, which is antistreptolysin O.
Although positive results are characteristic of Streptococcus pyogenes infection, not all people develop symptoms of rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis or tonsillitis, for example, however they should be accompanied by the doctor, performing periodic blood tests and cardiac checkup. See the exams requested to evaluate the heart.
How is done
The ASLO test should be done fasting for 4 to 8 hours according to the medical or laboratory recommendation and is done from the collection of a blood sample that is sent to the laboratory for analysis. In the laboratory the test is performed to detect the presence of antistreptolysin O in the blood, which is done by adding 20 μL of reagent, called ASO Latex, to 20 μL patient sample on a dark background plate. Then, the homogenization is done for 2 minutes and checked for agglutination of the particles in the plate.
The result is said to be negative if the antistreptolysin O concentration is equal to or less than 200 IU / mL, this result however may vary according to the laboratory in which the test was performed and the person's age. If agglutination is found, the result is positive and successive dilutions are necessary to check the antistreptolysin O concentration in the blood. In that case, the doctor may request a new examination after 10 to 15 days to check whether the antistreptolysin concentration decreases in the blood, is constant or increases, and thus to check whether the infection is active or not.
In addition to the ASLO examination, the doctor may request a microbiological culture of material from the throat, since it is the place the bacteria normally are present, to directly detect the presence of Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria.