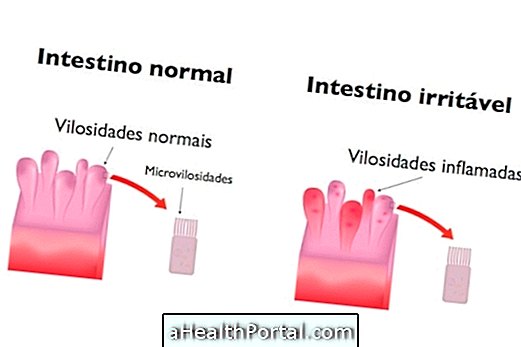
Celiac disease is the permanent intolerance to gluten present in food. This is because the body does not produce or produce little enzyme capable of degrading gluten, which causes a reaction of the immune system that results in lesions in the intestine.
Celiac disease can manifest itself in infants as they begin to vary their diet at 6 months or during adulthood and is characterized by diarrhea, irritability, fatigue, unwarranted weight loss or anemia without apparent cause.
There is no specific treatment for celiac disease, however, symptoms related to the disease can be controlled by eliminating any food or product that contains gluten or traces. Gluten may also be present in small amounts in toothpaste, moisturizers or lipstick, and people who have cutaneous manifestations when consuming gluten, such as itching or dermatitis, should also avoid these products. Therefore, it is always recommended to carefully read the labels and packaging to make sure the presence of gluten in the products. Learn where gluten can be found.

Symptoms of celiac disease
The symptoms of celiac disease vary according to the degree of intolerance of the person, usually:
- Vomiting;
- Swollen belly;
- Weight loss;
- Lack of appetite;
- Frequent diarrhea;
- Irritability or apathy;
- Large and bulky evacuation of pale and very smelly feces.
When the person has the mildest form of the disease, the symptoms of gluten intolerance manifest themselves through the following symptoms:
- Arthritis;
- Dyspepsia, which is the difficulty of digestion;
- Osteoporosis;
- Fragile bones;
- Short;
- Constipation;
- Irregular or absent menstruation;
- Feeling tingling in the arms and legs;
- Injuries to the tongue or fissures in the corners of the mouth;
- Elevation of liver enzymes with no apparent cause;
- Swelling that arises abruptly after infection or surgery;
- Iron deficiency anemia or folate deficiency and vitamin B 12;
- Bleeding gums when brushing teeth or flossing.
In addition, low levels of protein, potassium, and sodium in the blood can be noted, as well as impairment of the nervous system, leading to epilepsy, depression, autism, and schizophrenia. Learn more about gluten intolerance.
The symptoms of celiac disease disappear completely with the elimination of gluten from the diet. And to determine the diagnosis, the best doctors are the immunoallergologist, and the gastroenterologist. Here are the top 7 symptoms of gluten intolerance.
Diagnosis of celiac disease
The diagnosis of celiac disease is made by the gastroenterologist through the evaluation of the symptoms presented by the person and the family history, since the celiac disease is mainly caused by genetics.
In addition to the clinical evaluation, the doctor may request some tests, such as blood from blood, urine, stool and biopsy of the small intestine through a high digestive endoscopy. To confirm the disease, the doctor may also request a second biopsy of the small intestine after exclusion of gluten from the diet for 2 to 6 weeks. It is through the biopsy that the doctor can assess the integrity of the intestine and check for any signs that indicate gluten intolerance.
Treatment for celiac disease
Celiac disease has no cure, and treatment should be done throughout life. Treatment for celiac disease is made exclusively with the suspension of use of products containing gluten and a gluten-free diet, which should be indicated by a specialist nutritionist. See which foods contain gluten.
The diagnosis of celiac disease in adults is made when there is already a nutritional deficiency, so the doctor may indicate that supplementation of nutrients that may be lacking in the body due to the common malabsorption in celiac disease is done, in order to prevent other diseases such as osteoporosis or anemia.
Here's how the diet for celiac disease is made: