Symptoms of hepatitis may include nausea, loss of appetite, tiredness, headache and yellowing of the skin and eyes, and symptoms usually appear after 15 to 45 days after unprotected intimate contact or use of heavily soiled public restrooms.
There are different types of hepatitis such as Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, F, G, autoimmune hepatitis, hepatitis, chronic and contagious hepatitis and so the symptoms, form of contagion and treatment may differ from one case To the other. Learn more about the different types of hepatitis that exist in Types of Hepatitis.
Main Symptoms of Hepatitis
In most cases, hepatitis does not cause symptoms that are easy to identify. However, if you think you may be having this problem select what you are feeling, to evaluate the symptoms and to know what your risk is:
- 1. Pain in the upper right region of the belly Yes No
- 2. Yellowing of eyes or skin
- 3. Yellowish, grayish or whitish faeces Yes No
- 4. Dark urine Yes No
- 5. Constant low fever Yes No
- 6. Joint pain Yes No
- 7. Loss of appetite Yes No
- 8. Frequent dizziness or lightheadedness Yes No
- 9. Easy tiredness and no apparent reason Yes No
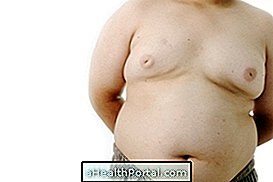
- 10. Swollen belly Yes No

All of these symptoms are more common in hepatitis A, B, D and E, and are not common in cases of hepatitis C, which can often be discovered only on routine exams.
In more severe cases, in addition to these symptoms may also appear a swelling on the right side of the belly, as the liver makes a greater effort to work, which leads to its increase in size.
When should I go to the doctor?
It is important to see a hepatologist when more than one of these symptoms appear, especially if you have yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine and light skin, swelling of the belly and upper right abdominal pain.
In these cases the doctor asks for blood tests, ultrasonography or computed tomography to confirm the diagnosis and correctly guide the treatment.
Here's what to eat to help cure this disease:

How to get Hepatitis
Hepatitis can be transmitted in several ways and the main forms of contagion include:
- Contact with contaminated blood;
- Contact with feces with the virus;
- Unprotected intimate contact;
- Use of public toilets;
- Ingestion of contaminated food;
- Lack of hygiene;
- Contact with doorknobs, discharges and taps of public places;
- Use of unsterilized materials to make tattoos, piercings or to make the nail for example;
- Raw food or raw meat.
These are the most common forms of hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, F, G, chronic and contagious hepatitis, as they are contagious and can be transmitted easily. Here are some ways to prevent hepatitis by clicking here.
On the other hand, drug hepatitis and autoimmune hepatitis are types of hepatitis that are not contagious, and can arise from causes such as alcohol or drug abuse, autoimmune diseases or due to a genetic predisposition to have the disease.
The treatment varies according to the type of hepatitis, the severity of the lesions and the form of contagion. However, in most cases the treatment is started with rest, hydration and a balanced diet with few fats. See how the treatment of some types of hepatitis is done by clicking here.