Toxoplasmosis is a disease caused by contamination with the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii. About 90% of people who are infected do not have any symptoms, but this infection is particularly severe in women during pregnancy because it can endanger the baby's life.
Women who have been contaminated before becoming pregnant can develop chronic toxoplasmosis and need not worry, but anyone who has never had contact with the micro-organism should be careful throughout pregnancy with everything they eat to avoid being contaminated at this stage, thus protecting the baby.
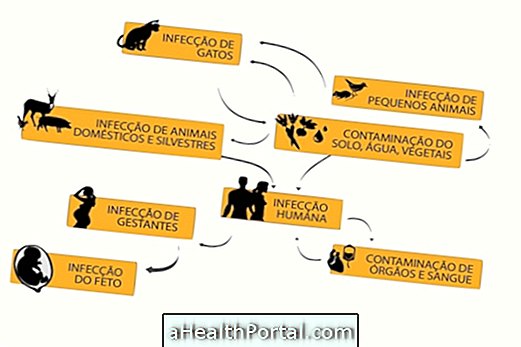
The types of toxoplasmosis vary according to the way the disease presents, and can be:
1. Acute febrile toxoplasmosis
In acute febrile toxoplasmosis, which is the most common form of the disease, the infected person usually does not have any symptoms and therefore does not need treatment. When there is manifestation of symptoms these may be red patches on the skin, fever and there may be symptoms such as diffuse pneumonia, dry cough, myocarditis and muscle pain while there is fever, abdominal pain and mild hepatitis.
2. Lymphatic toxoplasmosis
In mild lymphatic toxoplasmosis the disease manifests symptoms that include enlargement of a neck and armpit lymph node, malaise, muscle aches and low and fluctuating fever that can last for weeks or months. Discrete anemia, low blood pressure, low white blood cell count, and mildly abnormal liver function tests are common.
3. Disseminated Toxoplasmosis
It can produce rash, high fever, chills and extreme fatigue. It occurs mainly in individuals with impaired immune system as in those with AIDS, being common cause encephalitis, hepatitis, pneumonitis, myocarditis, meningoencephalitis, and as a consequence of the inflammations cause convulsions, tremors, headache, mental confusion or coma. Acute disseminated toxoplasmosis is the most common opportunistic infection in people with the HIV virus due to a reactivation of the cysts, mainly in the brain causing encephalitis.
4. Neonatal Toxoplasmosis
Neonatal toxoplasmosis is when the baby is infected during pregnancy leading to severe complications such as premature labor, low birth weight, liver, eye, lung and heart problems.
5. Toxoplasmosis of the eye
Ocular toxoplasmosis occurs in the event of contamination of the baby during pregnancy and can manifest itself at birth or years later causing severe damage to the eyes, especially when the optic nerve and macula are affected. Its treatment can be done with pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, folinic acid, in addition to corticosteroids prescribed by the doctor and aims to stop the loss of vision.
Generalized Toxoplasmosis
It is a very serious form of diseases that leads to death even when it affects healthy people, but it is rare.
How to protect yourself from toxoplasmosis
The only way to protect yourself is by cooking food well because there is no vaccine for human use against T. gondii infection, the only existing vaccine is for sheep.
In relation to contamination caused by cat feces this usually does not happen with domestic cats that do not hunt or feed on raw meat. Fresh cat feces, although they may contain oocysts, are not yet sporulated and therefore do not transmit toxoplasmosis. The greatest risk lies in the contact with the land where the cat buried its faeces, where the oocytes had time to be sporulated by the environment, and could contaminate the soil, the water of this soil and also the food produced in it. These can stay on the ground for up to 1 year.
Thus, to protect yourself from toxoplasmosis you need:
- Always perform gardening with gloves;
- Change daily the sand where the cat's faeces are and wash the container with hot water or chlorine every day;
- Wash well fruits, vegetables and legumes that are ingested raw;
- If you have cats at home do not let them eat raw meat.
In order to know if the person has already been contaminated with T. gondii should be carried out the blood test that finds antibodies against the protozoan.