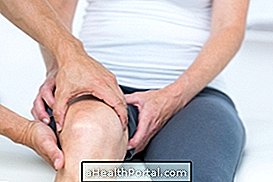
Joint effusion consists of the accumulation of fluid in a joint of the body, caused by strokes, falls, infections or chronic joint diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. Popularly it is called 'knee water'.
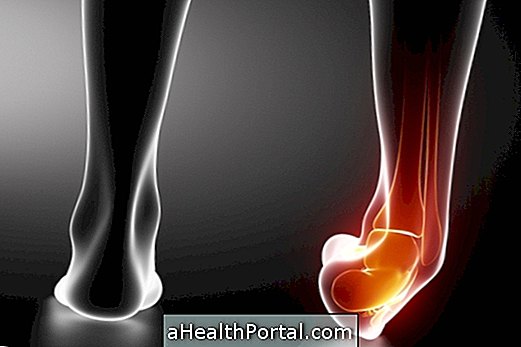
Generally, joint effusion is more frequent in the knee due to excessive use of this joint to run or walk, for example, causing knee swelling. However, the stroke can occur in any joint of the body such as ankle, shoulder or hip.
The joint effusion is healing, and usually the treatment is done with physical therapy to facilitate the absorption of the liquid, reducing its symptoms. At home, the person can put a cold compress for 15 minutes to lessen the local swelling. See: When to use hot or cold compress.
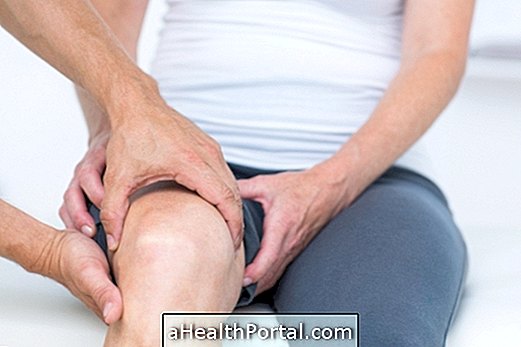
7 steps to treat joint effusion
The treatment of joint effusion should be guided by an orthopedist or physiotherapist and can be done with:
1. Protection and rest: As long as the pain persists, the painful joint should be protected. For example, when knee is affected, crutches or knee pads should be used until you can walk without pain;
2. Apply ice: Crushed ice packs are useful for disinfecting and relieving pain. Let it act for 15 minutes, putting a thin cloth around the ice pack so it does not burn the skin;
3. Bandaging: Bandaging the sore joint with a gauze making a slight pressure helps control the swelling;
4. Raise the affected limb: If your knees are swollen you should lie on the bed or couch and place a cushion under the knee so that the leg is tilted up;
5. Massage: The foot massage to the hip is effective in relieving pain and swelling;
6. Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Your doctor may prescribe Ibuprofen or Diclofenac, help reduce inflammation of the joint, decreasing pain. These remedies can be taken in the form of tablets or by injection (infusion) into the affected joint. It can also help take sucupira tea because it contains anti-inflammatory, anti-rheumatic and analgesic property. See more in: Sucupira tea for arthrosis and rheumatism.
7. Aspiration of the liquid: It can be used in the most severe cases to remove excess fluid with a needle in the doctor's office or in the hospital.
Physiotherapy for joint effusion
Physiotherapy involves practicing exercises that help strengthen the joint and improve blood circulation by draining excess fluid. These exercises should be appropriate to the affected joint and therefore it is important to receive guidance from a physical therapist.
Initially the exercises should be done slowly and progressively and it is also important to use the technique of joint mobilization, which consists of small joint movements that increase intra-articular lubrication and reduce cracking.
Exercises

Some knee joint exercises, which may be indicated by the physiotherapist, include:
- Stand and then slowly bend the affected knee, as shown in figure 1, and repeat 8 to 10 times, for 3 sets;
- Sit on a chair with both feet on the floor and slowly stretch the leg with the affected knee 10 times, repeating for 3 sets;
- Lie on a bed and put a rolled towel under the affected knee, then push the leg down without bending the knee and repeat 8 to 10 times, repeating for 3 sets.
It is recommended to make 30-second intervals between each series of exercises to avoid excessive joint wear and worsening of symptoms.
Also see everything you can do at home to treat your knee.
Symptoms of joint effusion
Symptoms of joint effusion may include:
- Swelling of the affected joint;
- Pain in the affected joint;
- Difficulty in moving the affected joint.
Symptoms may vary in intensity depending on the type of occupancy of the individual. The diagnosis of joint effusion is made by the orthopedist through observation of symptoms and examinations such as X-ray or MRI.