Aneurysms of the aorta are detected by examinations such as X-ray, ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging. Aneurysms of the aorta are dilatations that occur in this blood vessel and an important cause is atherosclerosis. Usually people who have aneurysms feel no symptoms and only find they are sick while taking an exam. The treatment is done with the follow-up of the cardiologist and in the most serious cases, with surgery, since there is a risk of the ruptured aneurysm causing bleeding, which can lead to death.
Symptoms of aneurysm
Most aneurysms have no symptoms and the patient only knows that he has an aneurysm when he goes to the doctor or performs an examination such as x-ray or ultrasonography. The symptoms depend on the location of the aneurysm, which can be:
- Ringing in the ear;
- Headache;
- Dizziness or dizziness;
- Somnolence;
- Lips, ears and nails with bluish color;
- Dry cough that does not improve even with the use of medicines. In some cases coughing may occur with phlegm elimination with blood;
- Tiredness and shortness of breath;
- Vomiting;
- Difficulty swallowing food.
The appearance of symptoms often means that the aneurysm is already more advanced, putting the life of the patient at risk. Therefore, in case of suspicion, you should go immediately to the emergency room.
Diagnosis of aneurysm in the aorta
Aneurysms of the aorta are usually difficult to detect and so specific tests are needed to make the diagnosis, such as X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography, aortography and magnetic resonance imaging. Even so, aneurysms can only be recognized when they already present complications, such as rupture.
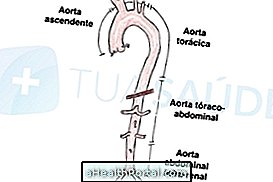
Aneurysms are dilatations of the aortic wall that make the artery weaker. As the aorta is a blood vessel that leaves the heart and runs throughout the body, aneurysms are classified according to their location, for example:
- Aneurysms of the thoracic aorta: they are located in the part of the aorta that is in the thorax;
- Aneurysms of the abdominal aorta: Locate in the part of the aorta that is in the abdomen.

Causes and consequences of aneurysms
Aneurysms can be caused by:
- Atherosclerosis, which are fat plaques that clog blood vessels;
- Syphilis in advanced stages;
- Injuries, such as car accidents or falls in which large shocks occur in the chest or abdomen;
- Congenital diseases such as Maritime Syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.
The main and most serious consequence of aneurysms is rupture, causing great blood loss and high risk of death. Having uncontrolled high blood pressure is a factor that worsens the aneurysm and increases the risk of rupture, so anyone who has high blood pressure should take the medications prescribed by the doctor and the diet indicated by the nutritionist. Check out 5 tips for controlling high blood pressure.
How To Treat Aortic Aneurysm
Treatment of aortic aneurysm depends on the severity of the case. Often treatment begins with the control of associated diseases such as hypertension and diabetes, but in more severe cases, when the aneurysm is large or breaks, surgery is needed. Learn more about how to treat aortic aneurysms.
See too:
- Symptoms of Heart Disease
- Diet for the heart
- Food that does the heart good